Check If Directory Exists In Linux With Bash
It’s useful to know how to check if a directory exists in linux from a bash script. A directory is a folder within a path in your linux system where all sorts of files and directories are stored. Your Music folder is a directory to store music files and your Downloads folder is a directory where all sorts files are downloaded from the web. You get the idea.
If Directory Exists
Lets start off with a simple example. You can copy all examples in this tutorial to a file and run the file yourself in a terminal to test for yourself.
Check if a directory exists:
#!/bin/bash
dload_dir=$HOME/Downloads
if [ -d "$dload_dir" ]; then
echo "$dload_dir exists"
else
echo "$dload_dir does not exist"
fiLets break down the sample above:
- The “$dload_dir” variable value is the default Downloads directory in the system.
- The “$HOME” linux built-in variable points to the path “/home/username/”.
- Left square bracket “[” is a “test” command.
- “-d” tells the test command to check if the file exists and if it’s a directory.
When you run the code above it will output the directory “exists” and “does not exist” if it doesn’t.
We will now do the opposite and check if the directory does not exist.
Check if a directory does not exists:
#!/bin/bash
dload_dir=$HOME/Downloads
if [ ! -d "$dload_dir" ]; then
echo "$dload_dir does not exist"
else
echo "$dload_dir exists"
fiThe sample above is nearly the same, but we add a “!” symbol and swap the two echo commands. The “!” symbol tells the test command to instead check if the directory does not exist.
Now that we’ve covered the basics to checking for a directory, lets get a little more advanced.
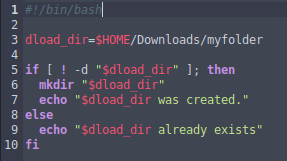
Check if a directory exists and if not, then create it:
#!/bin/bash
dload_dir=$HOME/Downloads/myfolder
if [ ! -d "$dload_dir" ]; then
mkdir "$dload_dir"
echo "$dload_dir was created."
else
echo "$dload_dir already exists"
fiIn the code above we use the “mkdir” command to create a new directory.
If you run the code above it will create a directory named “myfolder” in the Downloads directory and let you know it was created. If you run the code a second time, it will say that it already exists.
Check if a directory is empty:
#!/bin/bash
dload_dir=$HOME/Downloads
if [ "$(ls -A $dload_dir)" ]; then
echo "$dload_dir is not empty."
else
echo "$dload_dir is empty"
fiIn the sample above we use the list “ls” command with the “-A” flag which tells ls to list all files and directories including the hidden ones in the Downloads directory. If files or directories are found, it lets you know the directory is not empty.
Pass any directory to a bash script:
#!/bin/bash
my_dir=$1
if [ "$(ls -A $my_dir)" ]; then
echo "$my_dir is not empty."
else
echo "$my_dir is empty"
fiCopy the code above to a file and name the file “file.sh” then give the file execute permissions.
Now to use the script you just created, you pass it the directory you wish to check. Like this:
./file.sh $HOME/DownloadsIf you noticed, the variable has changed to “$1”. This allows the script to take one argument which would be the directory you pass to it.
You can use this script to check if any directory is empty by simply passing the directory to the script as demonstrated.
Conclusion
This brings the tutorial to an end. This was a quick look at how to do checks on directories in linux with bash.
Tags: tutorials, linux, command line